Room ivy is the most popular "residential liana", which, due to its unpretentious care, is very popular among gardeners. This plant will develop not even in the most favorable conditions for itself, for example, a pot with ivy can be put in partial shade, but for a certain period and in the shade, where any other flower will just die. Whether this plant is suitable for you and whether you are ready to provide suitable conditions, we will help to understand today's article.
Suitable landing site
As mentioned above, indoor ivy can continue to grow even in conditions that are not very favorable for themselves, but if there is a possibility, then this flower can best grow in partial shade, where diffused sunlight will pass for a couple of hours a day.
Tip: despite its shade tolerance, with a long shortage of sun, ivy can lose its decorative effect and variegation of color.
The main enemy of ivy is the direct rays of the sun, they leave severe burns on the leaves of the plant, after which the flower often begins to ache.
Tip: ivy does not like when it is often rearranged, especially if the light source changes.
The “room” liana perfectly reacts to fresh air and tolerates drafts well, so you should always regularly ventilate the room where the flower is located.
Optimal watering
This flower will calmly transfer, if you forget about it for a while, temporary drying of the earthy coma is not destructive for this plant. But of course, if there is a possibility, then the plant should be moistened on average once every 5-7 days in summer, and in winter - once every two weeks.
Tip: waterlogging of the soil in the pot for ivy is very dangerous, as it is fraught with various diseases, such as root rot.
Tip: if the room temperature is above + 24 degrees, the watering frequency should be increased.
Water for irrigation should be soft, rain, melt or the one that settled for a day.
Temperature and humidity
The main advantage of ivy - a painless reaction to the heating season in the room, because the plant is most often acquired by residents of apartments. In summer, the optimum temperature fluctuates within + 22- + 24 degrees, if the thermometer rises higher, you should increase the frequency of irrigation and raise the humidity level in the room. In winter, indoor ivy calmly tolerates lowering the temperature to 16 degrees.
Tip: if the summer was very hot and dry, then you should spray the plants every day.
The humidity level in the room is not critical for this pot, it calmly reacts to dry air and to humidified one.
Fertilization
For fertilizer indoor ivy suitable complex mineral fertilizers for decorative and deciduous indoor plants. Adding lure should be in the period of active vegetative growth, which lasts from early spring until mid-autumn, with a frequency of every two weeks.
Tip: in winter, it is better to allow the plant to rest and stop fertilizing altogether or to minimize this process, for example, once a month.

Plant transplant
Young room ivy, which has not yet turned three years old, needs a year-round transplant, but more mature representatives of this species do not need to be replanted more than once every 2-3 years. This procedure should be performed in early spring, the most favorable months are March and April.
Tip: The first sign that the plant needs urgent transplantation is entwining the roots of the whole earthen coma and a significant slowdown in growth.
When transplanting, you should find a larger pot than the previous one, at the bottom of which a drainage layer is poured.
Tip: drainage must be used for planting, because it avoids stagnation of water and provides oxygen access to the roots.
During transplanting plants need to update the land and be sure to make new fertilizers.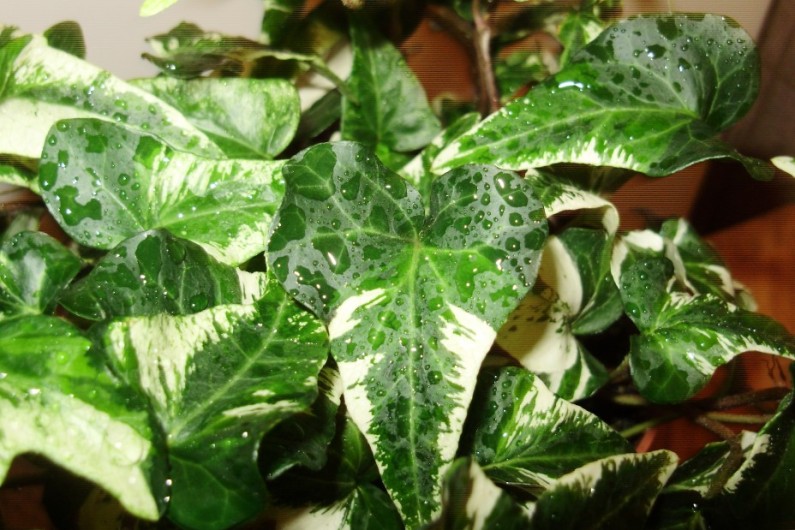 
Methods of reproduction at home
Reproduction cuttings
For this method it is necessary to cut the cutting off the ivy and put it into the water until the roots appear, then the plant is planted in the ground and covered with glass or film for the first time to create greenhouse conditions. As soon as the ivy takes root - it is transplanted into a pot and take care of it, like an adult plant.
Breeding shoots
Ivy is a vine, because it has long shoots, often used for breeding. For these, the whole shoot is cut and laid out on wetted soil, while the leaves remain on top and the stem goes a little bit into the ground. It is best to cover this design with glass or film, then ivy will root much faster.
Breeding taps
For this method, next to the grown ivy plants should be put a pot with wet soil, where a long shoot is shoveled, which should be cut on one side.
Ivy, or Hedera (Hedera), is a fairly small genus of the Araliaceae family (Araliaceae), numbering 15 species of creeping shrubs and lianas, common in almost all areas of the northern hemisphere with a mild climate.
The shoots are abundantly branching, thin, woody with time. Their length can exceed 30 m, but on condition that the plant has a support with which it can climb up, fixing itself on the surface with small adventitious air roots. Leaves petiolate, dense, leathery, two-type: on the flowering branches they are light green, simple, lanceolate, oblong or ovate; on non-flowering, dark green, angular-lobed with a heart-shaped base. Blossoming is plentiful and long, from the end of summer to the last autumn month. The flowers are small, inconspicuous, blind, yellowish-green, collected in branched apical inflorescences, umbrellas with a diameter of 3-5 cm. Fruits - black or yellowish spherical berries with 1 - 5th seeds.
Types of ivy
In room culture the most common is the typical representative of the genus - ( Hedera helix). It is curling, and in the absence of a support, with long, flexible shoots covered with glossy leathery leaves, decorated with a network of light veins. On fruitless shoots they are 3 - 5-lobed, on fruiting - simple, ovoid or rhombic-ovoid.
 Many species and varieties have been obtained from this species, according to some data, their number reaches 400. However, of all the variety, a rather limited number is suitable for indoor floriculture, characterized by small foliage and compact overall size. Among them are the following.
Many species and varieties have been obtained from this species, according to some data, their number reaches 400. However, of all the variety, a rather limited number is suitable for indoor floriculture, characterized by small foliage and compact overall size. Among them are the following.
With a single dark green color:
- ‘Annette’ - a five-lobed leaf plate, almost star-shaped, with a weakly heart-shaped base;
- ‘Chicago’ is a five-blade leaf plate, its star-shaped form is more pronounced than in the previous variety, but the upper “beam” is larger than the others;
- ‘Green Ripple’ is a three-blade sheet plate with a rounded base and a “trident” tip, the central portion is much longer than the side lobes;
- ‘Scutifolia’ - a three-lobed leaf plate with a heart-shaped base, but the lateral lobes are almost not expressed, due to which the leaf assumes an angular-oval shape;
- ‘Sagittaefolia’ is a stellate-shaped sheet with narrow lobes, while the upper one is much longer than the others, the middle ones are approximately two times shorter, and the lower ones are small.
Variegated:
- ‘Marmorata’ - a three-blade sheet plate with a heart-shaped base, its surface is covered with yellow-white spots, separate or merging;
- ‘Eva’ - the shape of a leaf plate is similar to ‘Annette’, but the leaf color is olive green with a white border;
- ‘Mona Lisa’ - five-lobed leaf plate, star-shaped, with a long large triangular central lobe, the leaves are light green, with a yellow edge;  - ‘Lutzii’ - three-lobed leaves, very wide (width significantly exceeds length), with a deeply heart-shaped base, their color is light green with dark green spots;
- ‘Lutzii’ - three-lobed leaves, very wide (width significantly exceeds length), with a deeply heart-shaped base, their color is light green with dark green spots;
- ‘Jubilee’ - three-lobed leaves with practically no pronounced pointed blades, due to which the leaf plate has an irregular rhomboid shape, its surface is dark green, with large shapeless yellow spots (or one large spot);
- ‘Harald’ - leaf plate not expressed five-lobed, two lower blades - rounded, the others - triangular, color dark green, with white border;
- ‘Glacier’ - the leaves are a bit similar to the previous variety, but the lower blades are even less pronounced, the color of the leaf plate is dark olive-green, with large light green spots along the edge;
- "Golden Juge" - a leaf plate of non-expressed five-lobed, with a large, wide-triangular upper lobe and small rounded lower ones, its surface is almost completely yellowish-white, with a slight impregnation of dark green spots;
- ‘Goldheart’ - three-lobed leaves, dark green, with a yellow central part.
With wavy edge:
- ‘Ivalace’ - dark green leaf plate, non-expressed five-lobed, with a strongly wavy edge;
- ‘Cristata’ - leaf plate dark green, five-lobed, regular, almost round, with a strongly wavy edge;
- ‘Clotted Cream’ - three-bladed leaves, strongly wavy, almost corrugated along the edge, their surface is dark green, with white border.

In addition to ordinary ivy, growers grow, although much less frequently Canary ivy (Hedera canariensis). Its small popularity is due to its large size - it is one of the largest vines in the genus of ivy, its leaf sizes reach 15 cm in length and 12 cm in width. The leaf plate is dark green, three-blade, but the lateral lobes are weakly pronounced. The most interesting are variegated varieties of this ivy and, in particular, `Gloire de Marengo '- with a wide white, as if spread on the sheet, border, and` Striata' - with dark green background of the leaf and large light green or yellow spots in the center.
In addition to the two described species, it is also possible to consider several garden ivy with a large variation in color and size due to selection.
Colchic ivy(Hedera colchica) differs even larger leaves than the previous form. In an adult plant, they reach a length of 25 cm. The leaf plate is practically solid, oval-triangular, with a weakly heart-shaped base and a barely planned division into three broad lobes. Species coloring is green, but variegated forms are popular in culture:
- ‘Dentata Variegata’ - leaves with a wide, shapeless, bright greenish-yellow edge;
- ‘Sulfur Heart’ - leaves with a large yellow spot in the center, as if casually applied with a wide brush, and slightly drooping edges;
- ‘Arborescens’ is a low compact vine with drooping shoots and light green oval whole-edged leaves.
Irish ivy(Hedera hibernica) is characterized by rapid growth and abundant branching. Heart-shaped leaves with a slightly wavy surface, with five mild triangular lobes. In the original form they are dark green, glossy, with light streaks, but there are varieties with a matte surface or light green color. The length of the sheet plate reaches 15 cm.

Shepherd's Ivy(Hedera pastuchovii) - rare protected species listed in the Red Book. Differs in the correct heart-shaped form of leaves, not divided into blades. But on one shoot, in addition to cordate, sometimes there are ovate and broadly ovate leaves. The length of the sheet plate is about 10 cm, the color is dark green.
Ivy care at home
Ivy is considered one of the most unpretentious plants. Not requiring special attention, he can adapt to various conditions of detention and survive even in apartments of very inept gardeners. These qualities have led to its widespread use not only in the greening of apartments, but also in offices, offices, those places where care for green pets is minimal. However, even such a hardy liana imposes a number of requirements on its owners.
Lighting. Species ivy with green leaves is accustomed to shading and can grow even at some distance from the windows. For normal development, it requires only 2500 - 2700 lux. Therefore, if the windows overlook the south, west or east side, it is better to place it in the depth (within reasonable limits) of the room. On the north side, on the contrary, it will feel good only next to the window glass.
The variegated forms require much more light, the best option for their placement is windows facing west or east. Otherwise, their bright color may fade or disappear altogether.
Temperature. The plant prefers a moderately warm content, at 22 - 24 ° C. However, in winter, in order to avoid strong pulling of internodes, which visually lead to bare branches, its growth should be slowed down by lowering the temperature to 13 - 15 ° C.

In the summer, it is advisable to take the plant to fresh air, to the garden or to the balcony, leaving it in a dark place. Ivy quietly transfers sharp fluctuations and temperature drops, as well as drafts, so there should be no problems with the choice of its location.
Watering. Ivy is very moisture-loving. Irrigation mode throughout the year should be such that the soil in the pot remains constantly slightly wet (but not wet). Obviously, in hot summers or in dry, well-heated rooms, he will need more water than in cool content or wet weather.
The quality of the water is not particularly demanding, but still with tap water before irrigation should be allowed to settle and warm up (cool) to room temperature.
Air humidityshould be moderate, about 35%. In winter, when the central heating radiators are operating, this figure becomes much lower, so ivy sprouts may require regular spraying.
It is advisable to periodically rinse the leaves under a warm shower. He will not only refresh the plant, but also wash away all the accumulated dirt and dust, which prevents him from breathing.
The soil. Find a soil for growing ivy - not a problem. It requires a loose subacid nutrient substrate and from ready-made soils, in a large assortment of flower shops offered, specialized soil mixes such as Begonia, Geranium, Schefflera, or universal, for decorative leafy plants are well suited for it. If you want to cook the planting mixture yourself, then we can recommend the following composition: sod, leaf soil, peat, coarse-grained river sand in a ratio of 2: 1: 1: 1.

Before planting, it is necessary to pour pebbles or expanded clay on the bottom of the pot to form a drainage layer, which prevents stagnant water at the roots.
Crop. Ivy is an actively growing plant, some of its species are capable of producing almost a meter increase in a year. Therefore, in order to preserve a compact, fluffy form, the vine will need regular pruning, which is carried out in spring or autumn, shortening the shoots by about a third of their length and cutting out old, polysivshie or dried branches.
Breeding. Throughout the year, the plant is easily propagated by top cuttings that are well rooted in any substrate. Rapid rooting goes even in a glass of water. For the prevention of rot in it, you can add a tablet of activated carbon.
In order to make the young ivy more lush, several cuttings are immediately planted in the pot, and their tops and the emerging young shoots are constantly pinch.

Pests and diseases. Most often the plant is affected, and. Chemical pest control agents such as Actellic or Fitoverm should be used to control pests.
Plush is practically not susceptible to diseases, but if the content conditions are violated, its appearance may suffer somewhat:
Yellowing of the leaves is due to excessive watering, especially at low temperatures;
- loss of variegation or bright color - due to lack of lighting;
- drying of the tips of the leaves - due to too dry air, lack of watering, high temperature.
Myths and Reality. Recently, many housewives themselves are trying to get rid of ivy in their apartments, and friends advise, calling ivy "muzhegonom" and attributing to him the ability to get rid of men in the house. However, no one has yet been able to confirm such a mystical possibility of this plant. But as a natural natural air purifier, it firmly occupies a leading position, removing from the room a couple of formaldehyde, which is full of modern furniture; benzene, which is present in varnishes, paints, solvents, and many other preparations necessary for household use; natural gas combustion products and many more toxins. So this liana is simply necessary for modern city apartments and offices.
Indoor ivy belongs to the family Araliaceae - Aralia. It is a lignified vine with climbing stems with the help of suckers. The plant has one feature: it changes with the appearance of the leaves with age.
Currently, there are about 450 varieties of indoor ivy. They differ in size, shape and color of the leaves. The flowers in ivy inconspicuous, small. At home, ivy blooms very rarely. Homeland ivy is Europe.
The most common types in home floriculture are:
Hedera helix ssp. canariensis - Canary ivy.
Canarian ivy is a large species of ivy, different dark red petioles of large, up to 20 cm long, leaves. The most popular variety of this species is the variety "Variegata": the beautiful white streaked leaves have provided popularity for it.
The height of ivy reaches from 100 to 200 cm and more.
Canary ivy needs regular but moderate watering, prefers partial shade and diffused light, air temperature is + 15 ... + 20 degrees. During the period of growth it needs weekly feeding. To enhance branching in young plants, pinching the tips of the shoot is done. Reproduction is performed by stem cuttings (link). Replant the plant once every 2-3 years.
Hedera helix - Common ivy.
 This type of ivy is used mainly for the decoration of the walls of buildings, as it is able to conquer any vertical surface.
This type of ivy is used mainly for the decoration of the walls of buildings, as it is able to conquer any vertical surface.
Once ivy is planted, it needs to be watered regularly until fully rooted, but that is if you do not use mulching. When mulching and the presence of fertile land, ivy is practically not watered, with the exception of non-precipitation of precipitation for a week or two.
What is mulching used for? First, it retains moisture and improves soil structure, prevents the emergence of weeds, and also maintains soil moisture and cools the soil. 5-10 cm of sawdust or hardwood compost is used as mulch.
 Nitrogen fertilizers can be used as fertilizers at the rate of 6 tablespoons per square meter of soil surface. Fertilize better ivy in spring. The main thing is not to overdo it, since an overabundance of nitrogen can lead to a loss of color (especially important for the “Golden Dust” varieties or the “Jubilee”).
Nitrogen fertilizers can be used as fertilizers at the rate of 6 tablespoons per square meter of soil surface. Fertilize better ivy in spring. The main thing is not to overdo it, since an overabundance of nitrogen can lead to a loss of color (especially important for the “Golden Dust” varieties or the “Jubilee”).
After a dry autumn, it is necessary to soak water in the soil where ivy grows. This is done so that the bright sun or strong wind does not lead to the "burning" of the foliage. Newly planted plants on the south side should be covered with white foil.
Ivy propagation
Ivy is propagated by cuttings and layering. A cut piece of the stem with a tip 10–15 cm long and 3-4 bottom sheets removed is placed in a glass of water 1/3 of its length, or in a pot with wet sand, vermiculite, or a mixture of well-mixed garden soil (1/3) and perlite (2/3).
Root formation usually occurs within 4-6 weeks. To check this, try to pull the leaves from the pot: if you feel resistance, then the roots have already formed exactly.
Basic rules for indoor ivy content:
The optimum temperature is +15 - +17 degrees;
Loves spraying and washing the leaves in the shower;
To maintain the necessary humidity in the winter, it is better to put the plant pot in a pallet with wet claydite or gravel;
During the period of vegetative growth it is necessary to feed a universal fertilizer once a week; in the winter - once a week.
Variegated ivy needs a lot of light, but direct sunlight and content in a dark place are contraindicated.
The question asked at the forum on the content of ivy at home:
During the winter, almost all of the shoots died at my ivy, the leaves fell off. Why did this happen?
Love NOSKOVA
An important factor in keeping heders in winter is coolness. The plant does not tolerate the hot dry air from the central heating radiators and may die, despite frequent spraying. If possible, ivy should be placed in a bright cool place, reduce watering, thus giving him the opportunity to rest. The optimum temperature at this time is + 10-12 degrees.
By the way, the summer heat also adversely affects the health of ivy. It is advisable in the warm season to take the plants "on vacation" on the balcony or loggia, putting in a place protected from direct sunlight. In the fresh air, the plants thrive, grow actively, foliage becomes more saturated color. Daily temperature drops, nighttime coolness, and more humid air than in the room help them in this. The shoots grow additional sucker roots, as in nature, and with their help attach to any projections and irregularities of the walls and climb up.
Breeding
 Rooting cuttings is best done at the end of summer. Cuttings 8-20 cm long are planted 2-3 pieces in a pot with a soil mixture of this composition: sod, humus soil and sand in equal proportions. After that, the cuttings are covered with a glass jar and sprayed and watered regularly.
Rooting cuttings is best done at the end of summer. Cuttings 8-20 cm long are planted 2-3 pieces in a pot with a soil mixture of this composition: sod, humus soil and sand in equal proportions. After that, the cuttings are covered with a glass jar and sprayed and watered regularly.
The second method of reproduction is that the cut-off shoots with 8-10 leaves are laid horizontally in the groove. The groove is 1.5-2 cm deep and is made in wet sand. The leaves remain on the surface of the sand.
On the tenth day, underground roots form from the air roots and the tip of the shoot begins to grow. Two weeks later, the shoot is removed from the sand and cut into cuttings with one leaflet and roots. 3 stalks are planted in small pots.
Transfer
Once every 2-3 years, the plant should be transplanted into a larger pot (2-3 cm in size should be larger than the size of the rhizome). Drainage, placed on the bottom of the pot, will provide access of water and air to the roots. The main composition of the soil used for transplantation is formed from: turf, leaf soil, humus, parts of peat and sand from the calculation (1: 1: 1: 1: 1).
Transplantation is better to do in the spring after a period of rest. In the first years of life, the plant is transplanted annually, in the future you can only change the top layer of soil. Transplantation should be done when you notice that ivy is stunted.
The question asked on the forum for the content of homemade ivy:
After transplanting ivy absolutely does not want to grow. For six months, released only a few new leaves. Why?
Galina ZHUKOVICH
Usually the heder grows quite quickly, I have some varieties for the season increased the length of the shoots by almost half a meter. Poor growth can be caused by several factors. May not fit the land. Hedera develops well in a slightly acid (pH 5.5-6.5) permeable light mixture of leafy soil, peat and sand (2: 2: 1). Heavy, over-nutritional mixtures lead to the inhibition of the plant. Drainage is required.
Pot for planting cheder need a small, corresponding to the size of the root system. The plant develops better in tight containers.
Insufficient illumination can also be a possible cause of poor growth of a transplanted plant. Hedera is, of course, shade-tolerant, but it develops better in bright ambient light, especially variegated varieties. Then the leaf stalks and internodes shorten, the foliage more densely covers the shoots, and the whole plant looks more attractive.
Certain details of care
With a lack of light, the leaves of ivy become faded to prevent this from happening, provide the plant with the necessary amount of light, but remember that ivy prefers diffused light rather than direct sunlight.
Special care is needed ivy in winter. High room temperature leads to dry air. Ivy feels great at an air temperature of + 15-17 degrees, while it needs abundant watering and is picky about humidity.
During the growing season, the plant needs additional feeding and, possibly, a transplant. Watch for growth, transplant as needed and feed the plant once a week.
Possible difficulties
Pests and diseases
With improper care, ivy is affected by spider mites and flaps.
The question asked on the forum for the maintenance of ivy in room conditions:
A spider web appeared on the ivy, and the leaves began to fall rapidly. Water moderately, spray whenever possible every day. Maybe it's a tick?
Alena Rybik
Tick simply "loves" heders. Adverse factors and costs of care, weakening the immune system of the plant, lead to the emergence of a spider and red mite. Dry air, high temperature and insufficient watering contribute to this. Mite spreads quickly and in 2-3 weeks is able to destroy the plant. Therefore, at the first signs of its appearance, it is necessary to carry out 2-3 treatments with an interval of 5-6 days with special acaricidal drugs (fitoderm, neoron, actellic, omayte), diluted according to the instructions, or in slightly higher concentration. It is better to alternate preparations. Carry out the treatment in fresh air. Before this, the plant can be washed under the shower (to remove the main part of the pests) and let the foliage dry.
From alternative means it helps me to cope with the mite solution of household soap, and better - the foam means for washing dishes. Apply on the leaves, leave for about an hour, then wash off. However, unlike the use of "chemistry", such procedures have to be carried out twice as much (about 5 treatments). A pot tied with a plastic bag. I advise you, without waiting for the occurrence of the tick, to carry out preventive treatments twice a year — in the spring (because the plant is weakened during the winter and the risk of damage is great) and in the fall before hibernation. It is also important to arrange plants for showers more often. Sometimes another i.e. no less malicious pest, the shield, can attack ivy. Thoroughly and repeatedly (as it is detected), I clean it manually with a cotton wool dipped in alcohol, and additionally spill the soil with aktar or tanrek.
More material on the topic section:
| Pahistahis Pachystachys (Pachystachys) is an evergreen perennial shrub introduced from the tropical rain forests of Central and South America. Its homeland is also the subtropical forests of East India, the coast of Australia. |
|
| Pelargonium I have been friends with flowers for a long time, since childhood. I grow a lot of them - both in the open field and in the house. There are time-tested pets and new-fangled exotic. But I want to tell you about one flower that my daughter calls a grandmother. This is pelargonium, geranium, roll ... |
|
 |
Platicerium It can be grown in traditional pot culture, especially young plants. But truly spectacular and, importantly, naturally fern will look in a hanging pots or basket. |
The ivy plant (lat. Hedera) is often called a serpentine, a chaletz, heder, a bindweed and a breechetan. Culture is part of the Araliae family. The origin of the name of the flower (literally spit, spit) is associated with the unpleasant taste of the plant. Culture is widespread in South and East Asia, as well as throughout the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus. Flower ivy grows in the form of a creeping vine. With the help of adventitious, aerial roots, the plant clings to other green spaces and walls. In their natural habitat, ivy prefer moist and poorly lit areas. The plant can be found in canyons, lowlands and on the slopes of rocks.
Ivy is a shade-tolerant, climbing plant.
Location selection
Ivy are hardy plants. The flower can be planted in a darkened area or indoors.
To preserve the bright color of variegated leaves, it is desirable to choose a well-lit place. In the summer, it is necessary to protect the foliage and shoots from the scorching direct sunlight.
Temperature conditions
Caring for indoor ivy involves providing a cool microclimate with a temperature in the summer period of about + 18 degrees. In winter - no higher than + 12 degrees.
In the warm spring and summer, you can take the plant to a balcony or a covered terrace. The plant copes with sudden changes in temperature and drafts.
How to water ivy
Indoor ivy is a moisture-loving crop. Since the rhizome of the flower is directly under the top layer of soil, it is necessary in the hot season to regularly sufficiently water the pot. Drying out a soil coma will lead to serious consequences. Watering is necessary in moderation. Swampy ground will cause root rot.
In the winter season, if the plant is located in a heated room, the number of waterings should not be changed. In a cool room you will need to reduce soil moisture.

In winter, the amount of watering should be reduced.
Air humidity
Houseplant ivy in a building with a temperature below +22 degrees can do without additional moisture environment. Increased dryness of the air is fraught with consequences. It is necessary to spray water periodically on the crop and artificially increase the water content in the medium.
How to care for ivy - the frequency of transplantation
It is necessary to replant room ivy in the first few years each spring. In the future, adult representatives can renew the ground every two or three years.
Determining the need for a transplant is very simple. If the roots have grown heavily or the culture has stopped its intensive development, then the time has come for ivy transplanting.
It is advisable to use the transshipment method. This way you can save the root system. A few hours before the procedure will need to moisten the soil in a pot. This will simplify the extraction process.
Adult flower is not necessary to replant in a new container. Sometimes it is enough just to change the top layer of the soil mixture.
Trimming heders
During the period of intensive vegetative development, the flower needs periodic pruning.

With ivy, you can create an amazing bonsai style miniature.
To give a spherical bush form, you need to cut long shoots as needed. You can protect the plant by timely cleansing the flower from the dried leaves. Pruned branches in the future should be used as cuttings for reproduction.
Features of care for indoor ivy can be found in the video:
Ivy in open ground
Breeders deduced frost-resistant subspecies that can withstand a sudden drop in temperature in winter (up to –15 degrees). Preferably planted in the street hardy varieties. Culture with variegated leaves more in need of warmth and sunlight.
Hedera makes no special requirements for the soil. Increased development occurs in fertile, moderately moist areas. Ivy is resistant to harmful emissions and excessive amount of dust, gas and smoke in the environment.
It is preferable to plant the plant in a container and in the summer to make a loggia or greenhouse.

In the summer, heder can be taken out to the greenhouse or on the open terrace.
Thus you can save the flower from sudden natural disasters.
The nuances of growing indoors
How to choose a container
You should choose a shallow tank with a wide diameter. This contributes to the development of superficial rhizomes.
The bottom of the pot should be covered with a layer of drainage material - foam, gravel or gravel. The container must have openings for draining excess water.
Top dressing ivy
Growing in containers and indoors depletes the soil. For proper development, heders need to periodically fertilize the plant.
From early spring and the entire summer season, fertilizer intended for ornamental crops should be applied at least twice a month.
Ivy has no marked rest period. Depending on the conditions created, it is necessary to reduce the number of feedings to once a month.
Should strictly follow the instructions. One extra dose of ingredients can cause yellowing and premature falling of the foliage.
Soil for culture
Despite all the simplicity of the plant, ivy develops faster in a weakly acid and loose substrate.

Ivy prefers loose, subacid substrate.
You can plant a flower in a universal soil mixture or prepare yourself one of the options:
- In equal parts should be mixed sod land, leaf humus, peat and medium-grained sand.
- Take one part of the humus and sod soil. Then mix with half a serving of sand.
Prevention and treatment of characteristic ivy problems
Culture is often affected by pests - thrips, scutes, spider mites (with red dots).
The first symptoms of infection are deformation and yellowing of the leaves.
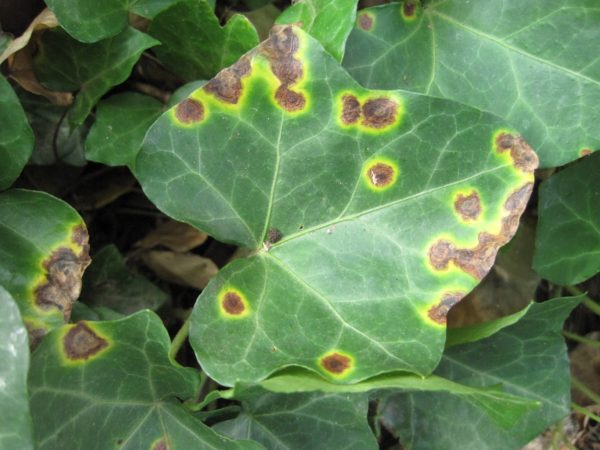

The consequence of improper care for ivy.
Inactivity leads to the death of the plant. To begin with, it is necessary to mechanically collect all pests. Then it is necessary to wash off the leaves left by pests. For treatment you will need to purchase insecticides.
Yellowness in different parts of the flower indicates excessive watering when the air is too cold in the room. Symptoms of a lesion may also indicate excessive use of supplements.
Variegated ivy sometimes gets a green color. Causes uncharacteristic shade, as a rule, a low level of illumination. It is necessary to change the location of the pot.
Low relative humidity at high temperatures causes dry leaf tips.
If a new foliage is unevenly formed in a plant or a large distance between parts of ivy, it is necessary to move the flower to a more lighted place.
Reaction to a flower
If the owner of the plant has a tendency to allergic manifestations, it is necessary to remove the inflorescences after the first signs of bud formation. The aroma of flowers cheder peculiar and unpleasant.

The aroma of inflorescences quite specific and unpleasant.
The juice culture includes strong components that cause allergic reactions. Dermatitis may appear on the skin after simple contact with the leaves. At the site of touch blisters form, itching begins.
Danger cheder is cumulative manifestation. After processing the plant may take more than a week. It is difficult to determine the source after a long amount of time. First of all, the lesion extends to areas of the face and hands.
If the irritation is not severe, you should take an antihistamine and limit contact with the plant. Severe lesions, including shortness of breath and fever, require immediate medical attention.
Ivy propagation
There are several ways to spread heders.
Cuttings
The most effective method of reproduction - cuttings. To do this, plant processes in the prepared container. The diameter of the tank should be about 7 centimeters. 2-3 pots should be placed in each pot. To preserve moisture, cover the container with plastic tops.
Sand and leafy soil is ideal as a soil mix. For planting, it is preferable to choose planting material with air roots.
It should be remembered that the variegated garden varieties to propagate in this way is very difficult. As a rule, cuttings are not rooted.
Breeding shoots
Get heder can be using the whole stem. To do this, escape with 10 leaves must be put in a container with sand and gently press. Branch leaves must remain on top.
Ten days later, the rudiments of underground roots will appear next to the kidneys. It is necessary to get the stem and cut it into pieces. Each segment must contain both leaves and roots.
Unlike other plants, it is not necessary to keep a branch in warm water beforehand. You can handle the cutting growth stimulator. Lack of adventitious roots can lead to a longer reproduction process.
Ivy breeding layering
Long branches can be notched on one side and stuck to the ground. It should be fixed in the ground with a clamp. After rooting, the retainer is removed and the new ivy is carefully transplanted.
Why the header does not bloom
The main reason for the absence of inflorescences is the removal of pedicels. On the side shoots many years in a row formed buds.
Produce inflorescences can only healthy strong representatives of ivy. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure optimal conditions for growing the culture.
How to choose ivy
The culture should be selected according to the variety and type of cultivation. There are subspecies intended for cultivation in room conditions and open ground.

Ivy must be selected according to the variety and method of cultivation.
Curler heading in a container with a diameter of 13 cm, a total height of 90 cm can be purchased at a price of 1,512 rubles. The price for ivy "Green cascade" is about 24 rubles.
Every woman loves homemade flowers. Of course. it's nice when the house is just full of green and rich colors of various plant species. This gives your home not only a lovely view, but also comfort, in which you really want to be. For everything to be greened, you need to know many rules for the care of each flower, and, of course, a lot of desire and patience.
One of the many and very charming plants is ivy, care at home does not seem to be a problem for you. This is an unusually elegant plant from the family of curlers, which can decorate any part of your apartment. Ivy was brought to us from the mountainous places of Asia. Most often, ivy grows in a forested area, and trees and rocks surround it with its beauty.
Plant Care
Depending on the species that you grow at home, it should be noted that every plant needs its own lighting. The motley forms of ivy strongly love the light of the sun, but the sun must not be allowed to come at a right angle Also absolutely all types of this plant do not celebrate change with light. But in the winter, ivy more than ever needs good lighting. If its quantity is insufficient, the leaves will lose their color and will not be so attractive. For such a flower in winter you need artificial light.
Ivy likes average air temperature. In summer, the air should not be too hot, from 20 to 25 degrees, and in winter, the best temperature for a flower is about 15 degrees. Accordingly, if in winter the temperature is high, then the plant should be watered a little more often. This type of ivy, as with variegated leaves is much more sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Drafts for any kind are completely undesirable. But the seasonal temperature is better to change gradually, rather than abruptly, it can affect the appearance and growth of the plant.

Humidity is one of the integral parts in the care. Because of this, he is always good at spraying his leaves. Such a procedure, especially in the hot season, has a good effect on the development of a decorative flower. If in the winter time ivy is located near the heating devices, then frequent spraying is also desirable. Dust on ivy leaves also needs to be collected at least occasionally, in the summer you can just put it under the shower. It is especially important that watering and spraying occur not chlorinated water, as it is very harmful to the plant.
When ivy is actively growing, it occurs from March to September, it is simply vital that various kinds of top dressing are needed, it is necessary to water it with fertilizers once a week. There are special fertilizers for decorative flowers. In winter, ivy can not be fertilized at all, or at most once a month.

Plant transplant
For this plant, almost every earthen mixture, which consists of peat, sand, and sod land, is suitable. Also, do not forget about the drainage, which must be put on the bottom of the pot. For young plants, transplanting is needed once a year or as needed. For older plants, a transplant is needed only when its roots no longer fit in a pot. Also, you should know that when transplanting, you must clean rotten and dry roots.

Plant propagation
Ivy can be well propagated by cuttings and layering. The cuttings that have sprouted from above must be cut off when they have reached 10 centimeters in length. Rooting occurs in almost any soil where there is enough moisture. Also, seedlings should be covered with a plastic bottle or plastic wrap, and observe the temperature from 18 to 22 degrees.
In order to propagate stalks, you need to cut the "liana", which should be about 10 leaves. This "liana" should be planted in the sand, and after 2 weeks, when the roots have already appeared, it can be transplanted into a pot.
Do not forget that all the flowers love when they are well looked after, and in gratitude give you their beauty. Ivy is not a capricious plant that just loves moisture. With minimal care, you will receive an amazingly beautiful decorative flower that will decorate your house and equip it with a pleasant look.
